

Note: The terratest_log_parser requires an explicit installation. See Installing the utility
binaries for installation instructions.
If you log using Terratest’s logger package, you may notice that all the test outputs are interleaved from the
parallel execution. This may make it difficult to debug failures, as it can be tedious to sift through the logs to find
the relevant entries for a failing test, let alone find the test that failed.
Therefore, Terratest ships with a utility binary terratest_log_parser that can be used to break out the logs.
To use the utility, you simply give it the log output from a go test run and a desired output directory:
go test -timeout 30m | tee test_output.log
terratest_log_parser -testlog test_output.log -outputdir test_output
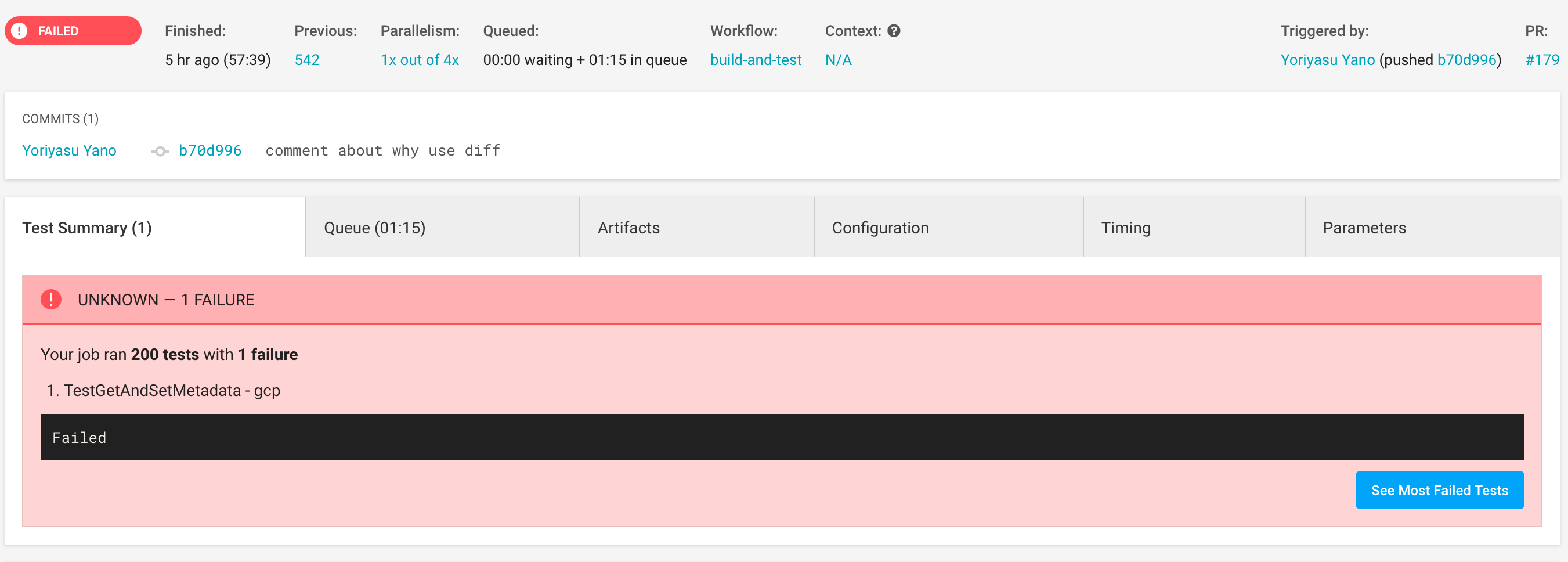
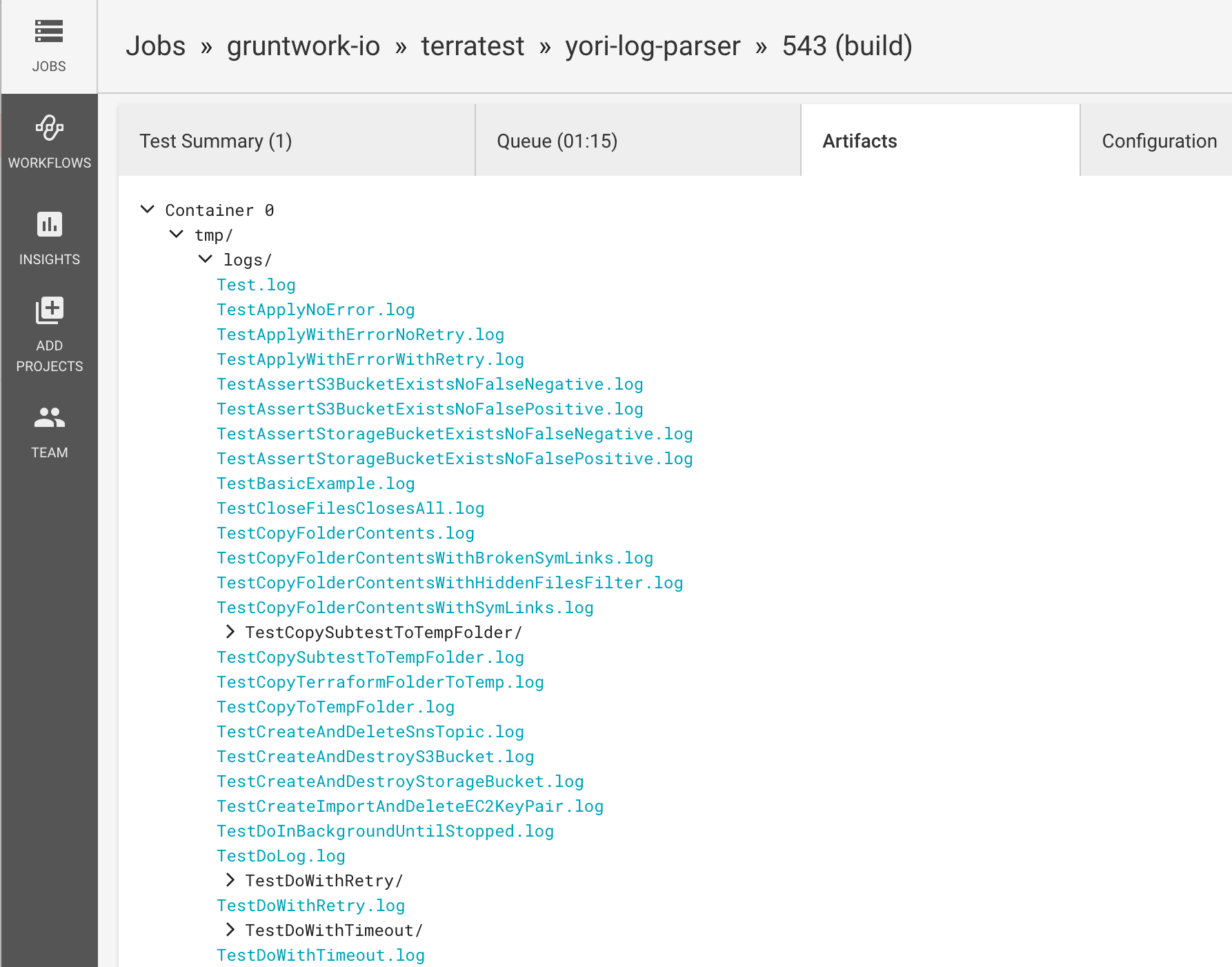
This will:
TEST_NAME.log for each test it finds from the test output containing the logs corresponding to that
test.summary.log file containing the test result lines for each test.report.xml file containing a Junit XML file of the test summary (so it can be integrated in your CI).The output can be integrated in your CI engine to further enhance the debugging experience. See Terratest’s own circleci configuration for an example of how to integrate the utility with CircleCI. This provides for each build:
Terratest also ships utility binaries that you can use to improve the debugging experience (see Debugging interleaved test output). The compiled binaries are shipped separately from the library in the Releases page.
The following binaries are currently available with terratest:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| terratest_log_parser | Parses test output from the go test command and breaks out the interleaved logs into logs for each test. Integrate with your CI environment to help debug failing tests. |
| pick-instance-type | Takes an AWS region and a list of EC2 instance types and returns the first instance type in the list that is available in all Availability Zones in the given region, or exits with an error if no instance type is available in all AZs. This is useful because certain instance types, such as t2.micro, are not available in some newer AZs, while t3.micro is not available in some older AZs. If you have code that needs to run on a “small” instance across all AZs in many regions, you can use this CLI tool to automatically figure out which instance type you should use. |
You can install any binary using one of the following methods:
To install the binary manually, download the version that matches your platform and place it somewhere on your PATH.
For example to install version 0.13.13 of terratest_log_parser:
# This example assumes a linux 64bit machine
# Use curl to download the binary
curl --location --silent --fail --show-error -o terratest_log_parser https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terratest/releases/download/v0.13.13/terratest_log_parser_linux_amd64
# Make the downloaded binary executable
chmod +x terratest_log_parser
# Finally, we place the downloaded binary to a place in the PATH
sudo mv terratest_log_parser /usr/local/bin
go supports building and installing packages and commands from source using the go
install command. To install the binaries
with go install, point go install to the repo and path where the main code for each relevant command lives. For
example, you can install the terratest log parser binary with:
go install github.com/gruntwork-io/terratest/cmd/terratest_log_parser@latest
Similarly, to install pick-instance-type, you can run:
go install github.com/gruntwork-io/terratest/cmd/pick-instance-type@latest
You can also use the gruntwork-installer utility to install the binaries, which will do the above steps and automatically select the right binary for your platform:
gruntwork-install --binary-name 'terratest_log_parser' --repo 'https://github.com/gruntwork-io/terratest' --tag 'v0.13.13'
Your entire infrastructure. Defined as code. In about a day.
Explore Gruntwork.io